Understanding the differences between Heavy Duty Motors and standard motors is essential for selecting the right solution for industrial, construction, and heavy machinery applications. From a manufacturer's perspective, these differences go beyond simple size or power rating—they involve design, materials, construction, and intended operating environments. This guide explores these aspects in detail, focusing on Heavy Electric Motor, Heavy Duty Motor, and Construction Electric Motor applications.
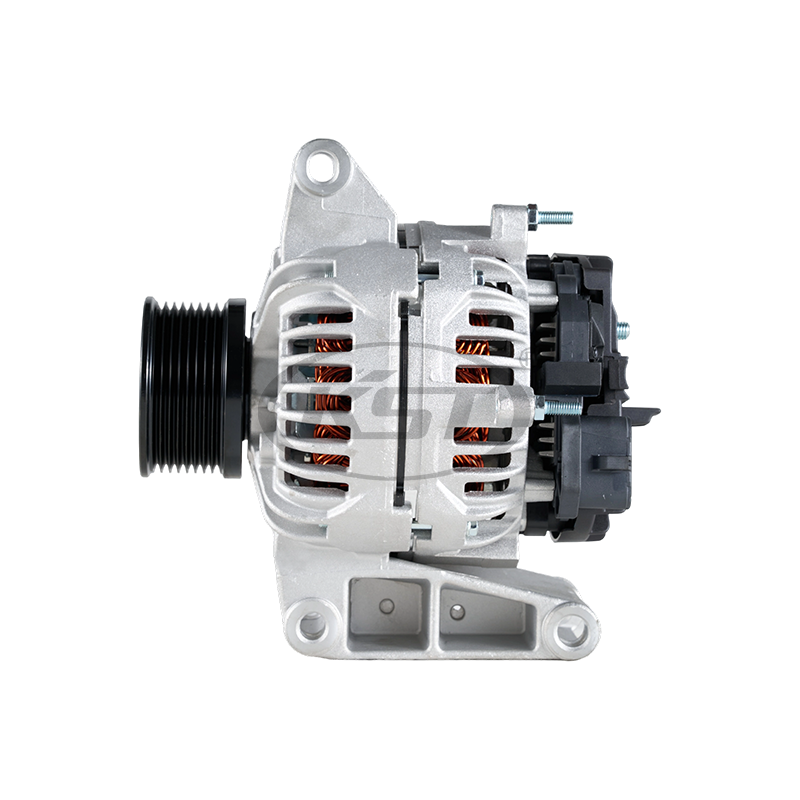

What Defines a Heavy Duty Motor?
A Heavy Duty Motor is designed for continuous operation under high stress, demanding mechanical loads, and harsh environmental conditions. Unlike standard motors, which are often used for light or intermittent applications, heavy duty motors are built to endure conditions and extended operational cycles.
Key characteristics include:
- Reinforced housing and frame to withstand vibration and mechanical stress
- High-quality bearings capable of supporting higher radial and axial loads
- Enhanced cooling systems for prolonged operation
- Durable insulation to prevent electrical breakdown in challenging conditions
Manufacturers design Heavy Electric Motor units specifically for industries such as mining, construction, steel production, and large-scale material handling, where reliability and longevity are critical.
How Does a Construction Electric Motor Differ From Standard Motors?
A Construction Electric Motor is a type of Heavy Duty Motor optimized for construction machinery, including cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers. While standard motors may fail under vibration, dust, and temperature extremes, construction electric motors are engineered to handle:
- Dust and dirt exposure from open work sites
- High vibration levels from heavy machinery operation
- Temperature extremes caused by outdoor or engine-adjacent installation
The design of a Construction Electric Motor often incorporates reinforced rotor shafts, protective enclosures, and specialized bearings to ensure the motor maintains performance under demanding operating conditions.
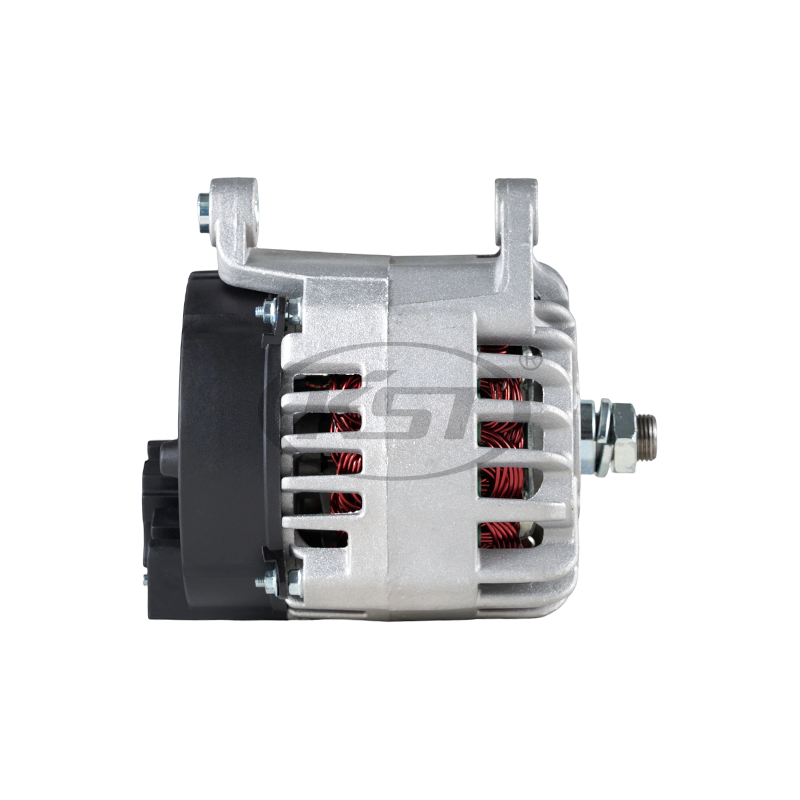

What Are the Mechanical Differences Between Heavy Duty and Standard Motors?
Mechanical design is a major differentiator. Manufacturers of Heavy Duty Motors emphasize components that extend service life and reduce maintenance. Differences include:
Heavy duty frames are thicker, made of reinforced steel or cast iron
Standard motor frames are lighter and less rigid
Heavy duty motors use bearings with higher load ratings
Standard motors are designed for moderate mechanical stress
- Rotor and Shaft Construction
Reinforced shafts and rotors prevent bending or fatigue under high torque
Standard motors may deform if overloaded
Fans, vents, or liquid cooling systems are optimized for continuous operation
Standard motors often rely on basic ventilation
These mechanical differences allow Heavy Electric Motors to operate reliably for thousands of hours in harsh conditions, while standard motors may require frequent maintenance or early replacement.
How Do Electrical Characteristics Differ Between Heavy Duty and Standard Motors?
From a manufacturer's perspective, Heavy Duty Motors are also electrically distinct from standard motors:
Heavy duty motors use high-grade insulation materials to resist heat, dust, and moisture, protecting against winding failure. Standard motors may only support short-duration operation.
- Voltage and Current Ratings
Heavy Electric Motor units are designed for higher voltage and current to handle demanding loads. Standard motors typically operate at lower ratings suitable for light-duty tasks.
Heavy duty motors provide higher starting torque, essential for moving heavy machinery or materials. Standard motors may struggle under sudden high-load starts.
Continuous duty (S1) motors, common in heavy duty applications, can operate indefinitely under full load. Standard motors are often rated for intermittent duty (S2 or S3).
Why Are Heavy Duty Motors More Reliable in Industrial Applications?
Reliability is a key concern in industries relying on Heavy Electric Motors. From a manufacturer's perspective, these motors are built with:
- Reinforced enclosures to protect against dust, water, and chemical exposure
- High-quality bearings that tolerate vibration, axial, and radial loads
- Advanced cooling and ventilation systems to prevent overheating
- Robust electrical insulation to prevent short circuits and ground faults
For construction machinery, using a Construction Electric Motor instead of a standard motor reduces downtime and maintenance costs, improves efficiency, and ensures consistent operation even under workloads.
How Does Maintenance Differ Between Heavy Duty and Standard Motors?
Maintenance requirements also differ significantly:
Require regular lubrication of high-load bearings
Periodic inspection of insulation and rotor windings
Scheduled replacement of components subject to wear
Less intensive lubrication schedules
May require complete replacement sooner under heavy use
Manufacturers often provide detailed maintenance guidelines for Heavy Electric Motor and Construction Electric Motor units to improve uptime and reduce unexpected failures.
What Applications Require Heavy Duty Motors?
Industries and scenarios where Heavy Duty Motors are essential include:
- Construction Sites: Cranes, concrete mixers, excavators, and hoists
- Mining Operations: Conveyor belts, ore crushers, and pumping systems
- Manufacturing Plants: Heavy presses, rolling mills, and extrusion machines
- Material Handling: Large fans, pumps, and compressors
In contrast, standard motors are suitable for light machinery, HVAC systems, small pumps, and office equipment.
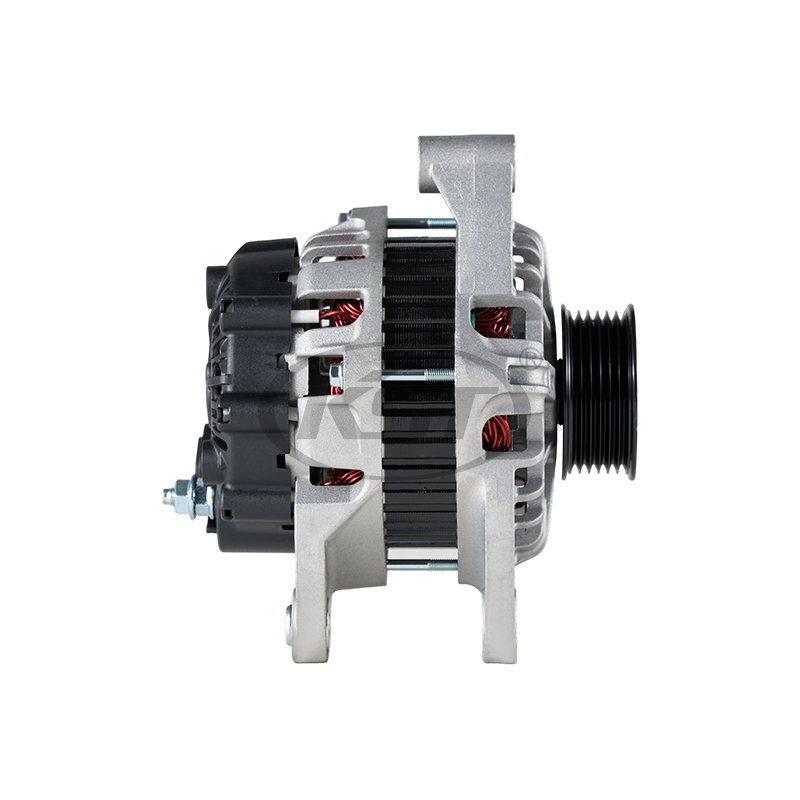

How Do Environmental Conditions Affect Motor Selection?
Environmental factors play a crucial role in selecting Heavy Duty Motors:
- Dust and Dirt: Construction electric motors feature sealed enclosures or filters
- Temperature Extremes: Heavy duty motors have thermal protection and specialized cooling
- Moisture and Corrosion: Coatings and insulation prevent electrical and mechanical failure
Standard motors may fail quickly under these harsh conditions, emphasizing the importance of selecting the correct Electric Motor Equipment for each application.
What Are the Cost Considerations?
From a manufacturer's perspective, Heavy Duty Motors and Construction Electric Motors have higher upfront costs compared to standard motors. However, the total cost of ownership is often lower due to:
- Longer lifespan
- Reduced downtime
- Lower maintenance frequency
- Increased operational efficiency
For industrial users, investing in a Heavy Electric Motor pays off over time, especially in critical operations.
How Do Heavy Duty Motors Enhance Safety?
Using the right motor also improves workplace safety:
- Stronger housings reduce risk of mechanical failure
- High-quality insulation prevents electrical hazards
- Stable operation prevents unexpected shutdowns
A Construction Electric Motor designed by a reputable manufacturer minimizes risks to personnel and equipment alike.
What Are Emerging Trends in Heavy Electric Motors?
Manufacturers are now focusing on improving Heavy Duty Motors with features like:
- Smart monitoring systems for real-time diagnostics
- High-efficiency designs to reduce energy consumption
- Compact but powerful construction motors for space-constrained applications
These innovations further distinguish Heavy Electric Motor and Construction Electric Motor offerings from standard alternatives.
From design and materials to performance, reliability, and maintenance, Heavy Duty Motors and Standard Motors serve very different purposes. A Heavy Electric Motor or Construction Electric Motor is engineered to operate under conditions, provide high torque, and withstand mechanical and electrical stresses. Standard motors are suitable for light applications but are not designed for heavy industrial or construction environments.
For manufacturers, the emphasis is on durability, efficiency, and reliability. Selecting the appropriate motor type ensures operational continuity, cost efficiency, and safety, especially in demanding industrial and construction applications.

 en
en  English
English عربى
عربى فارسی
فارسی